All About Your Muscle Anatomy

Your muscles are constantly working inside and around your body. Some are in your control, while others work automatically. What do your muscles do? How many muscles do kids have? Let’s learn all about your amazing muscles and their anatomy names.
What do muscles do?
Your mighty muscles are all about making moves! Muscles are organs that move other organs, tissues, and cells in the body.
During the day, they help you get up and move wherever you want.

Muscles are also moving nonstop inside your body whether you’re awake or asleep. They help your lungs breathe, make your heart pump blood, and carry food down your digestive tract.
Each muscle’s job depends on two things:
- The type of muscle cell
- The location in your body
How many muscles are in the human body?
Babies are born with around 600; the number stays the same when you transform into a kid, teenager, and adult.
How many types of muscles do kids have?
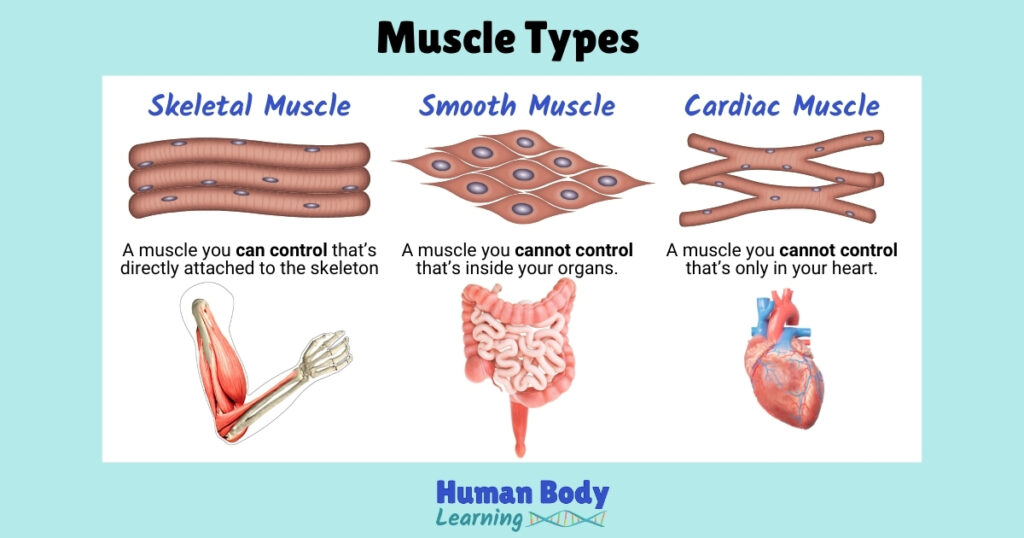
All people, including kids and babies, have three types of muscles in their body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
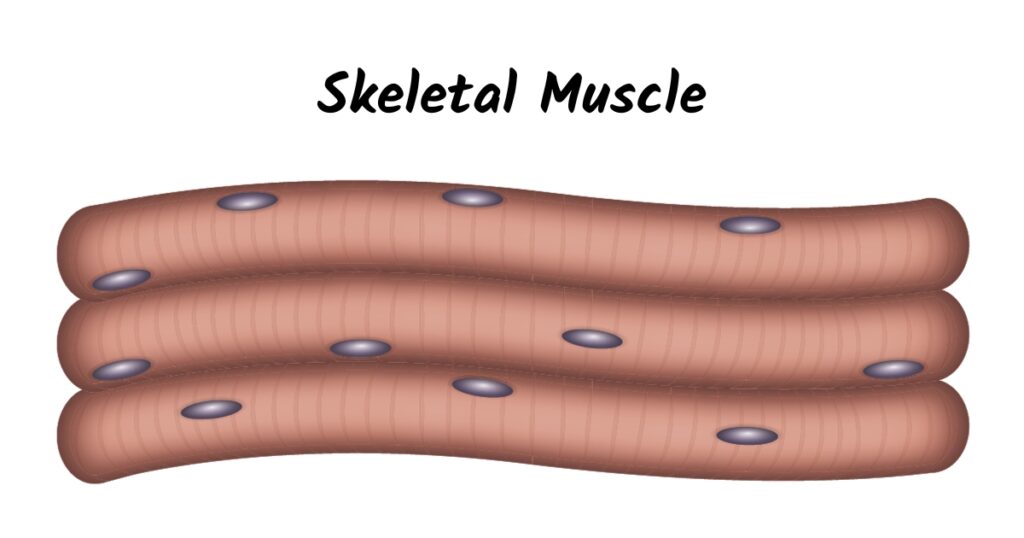
1. Skeletal muscle
When you hear the word “muscle”, this is the type that most people talk about. Skeletal muscles are famous because you can feel and flex them. These muscles move your body around the park. They help you carry your books and do your chores.
Most skeletal muscles are attached to your bones. You can move your face, neck, back, arms, legs, and other body parts by squeezing and relaxing these muscles.
They are also known as voluntary muscles since you decide when to use them.
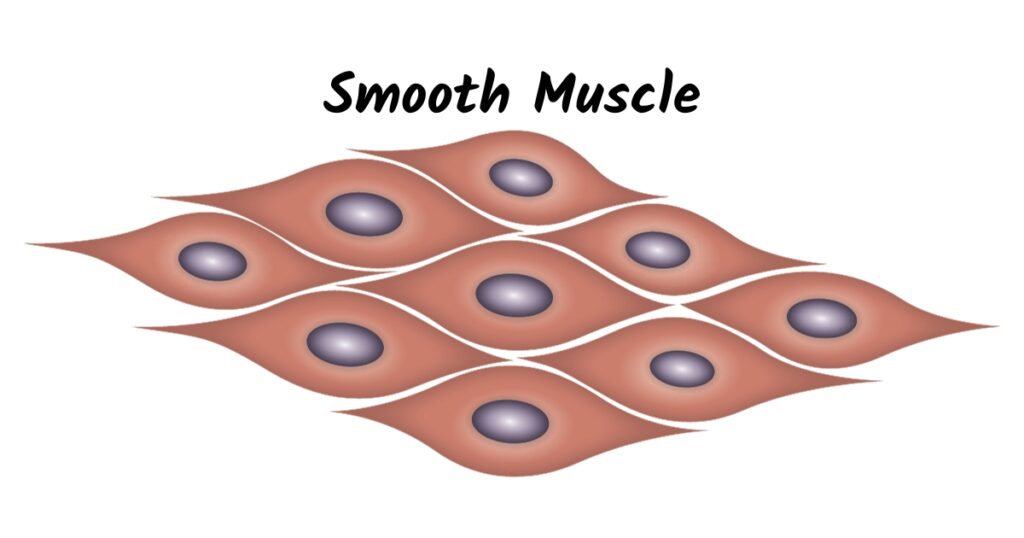
2. Smooth muscle
Smooth muscles are like secret superheroes inside your body. You can’t see them, but they work nonstop around the clock.
They line the inside walls of organs like the blood vessels, bladder, esophagus, stomach, and intestines – to name a few.
You don’t need to worry about controlling smooth muscles because your brain does that automatically. They are known as involuntary muscles since you can’t control them with willpower.
Smooth muscles are also not attached to your skeleton.
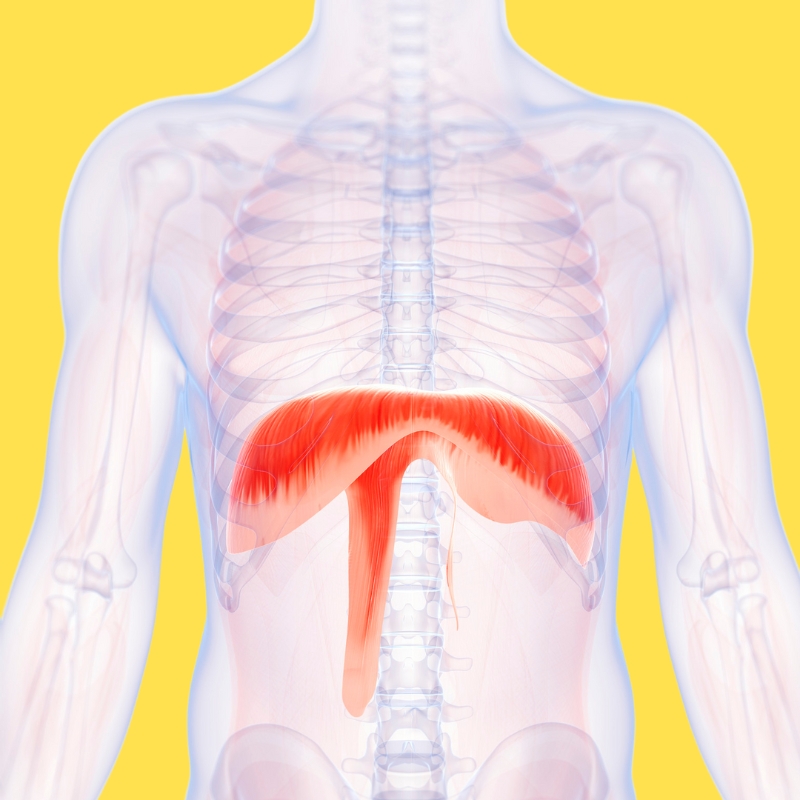
3. Cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle is truly one-of-a-kind. The heart is the only one in the human body, and it’s not attached to any bones.
Your heart automatically relaxes and squeezes to pump blood to all your organs, so this muscle is also involuntary.
Your heart automatically slows down when your skeletal muscles slow down, like during sitting or sleeping. It automatically speeds up when your skeletal muscles rev up, like during running or jumping.
What are the names of the major skeletal muscles?
Here are some important anatomy names to learn.
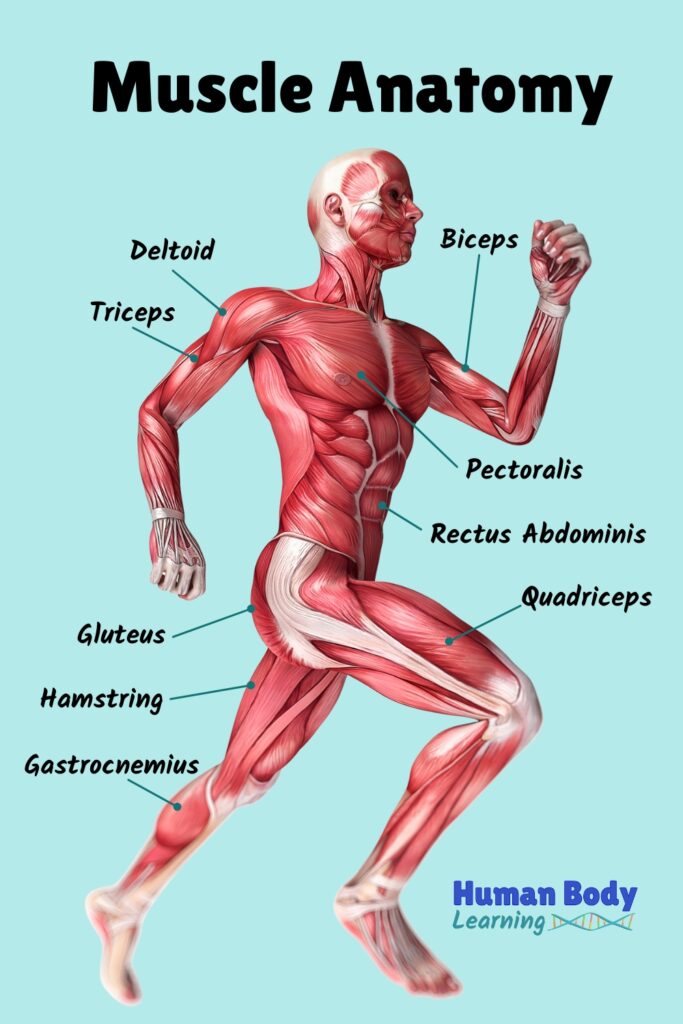
Arms
- Your biceps are in your front upper arm. When people say, “Flex your muscles!” they are referring to your biceps.
- Your triceps are in the back of your upper arm.
- Your deltoids are in your shoulders.
Chest
When you do pushups, you use the pectoralis muscles in your chest.
Abdomen
Your belly muscles are called rectus abdominis or “abs” for short.
Buttocks
The gluteus muscles in your bottom are among the strongest in the human body.
Legs
- The quadriceps, or “quads,” are in the front of your thigh.
- The hamstrings are in the back of your thigh.
- The gastrocnemius is in your calf.
How do muscles get stronger?
Want to know the secret to getting healthy and strong? The key is to exercise, eat healthy, and protect your body.
Exercise
The more you move your body, the stronger you will become. Soccer, tennis, and basketball are fun ways to exercise with friends. Dance, gymnastics, and other artistic exercises for kids are wonderful ways to boost strength and flexibility.
Eat healthy
Fruits, veggies, whole grains, beans, nuts, and fish are nutritious foods
Protect your body
These tips might seem to focus on skeletal muscles, but they also help your smooth and cardiac muscles.

How much exercise do kids need?
It depends on how old you are.
Playing throughout the day is a good idea for little ones in preschool. Think two or three hours of moving and grooving – like chasing bubbles or running around.
Life is busier in elementary, middle, or high school. You have to balance recess with classroom learning. Doctors recommend aiming for at least one hour of exercise at least three times a week. Awesome ideas include playing chase or having a dance party!
Learn more about your amazing anatomy!
Published on December 14, 2023. Updated on January 18, 2024 by Betty Choi, MD
Published on December 14, 2023. Updated on January 18, 2024 by Betty Choi, MD

Betty Choi, MD
Dr. Betty Choi is a Harvard-trained pediatrician who makes learning fun and doable. She created the kids’ anatomy book Human Body Learning Lab, which Science Magazine recommended as a “notable standout in the genre.”