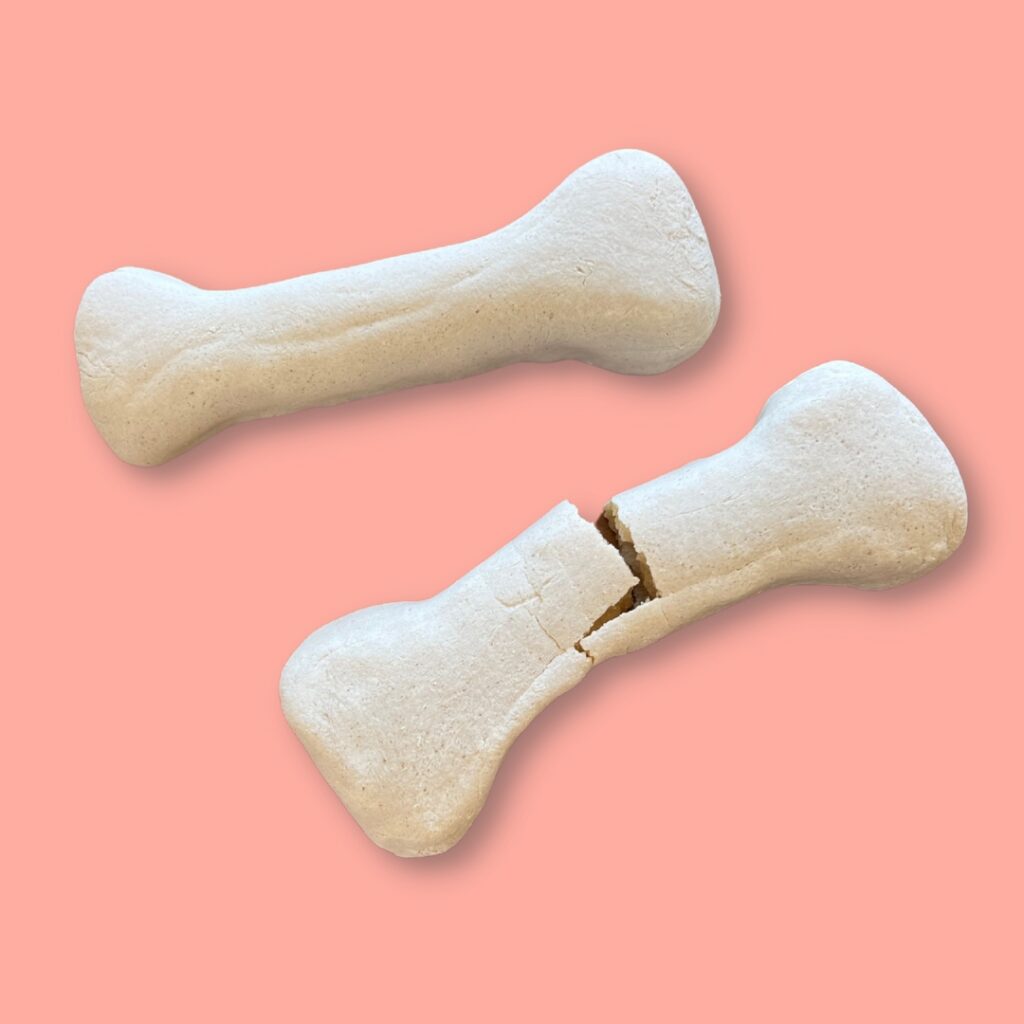
What is Cartilage and What Does it Do?
Cartilage is a special connective tissue that’s similar to bone. It also has a lot of important differences that are useful for protecting bones and helping kids grow. Keep reading to learn about the purpose of cartilage and why it’s amazing.
All about cartilage for kids
Imagine walking barefoot on a soft carpet and then hard concrete. Which would feel more comfortable to you?
The soft carpet, of course!
In your skeleton, cartilage acts like a soft carpet.
Because the purpose of cartilage is to make you feel protected and comfortable, people also compare it to pillows or cushions.
How is cartilage different than bone?
Cartilage and bone look, feel, and act differently.
More flexible.
Bone is hard and stiff, but cartilage can bend a little to cushion the weight of things pressing against it. Cartilage also feels smooth, so your bones don’t rub against each other.
No nerves or blood vessels.
This is a big difference! While bones have lots of nerves and blood vessels, cartilage does not.
What parts of the body have cartilage?
You can find cartilage throughout the human body! Here are just a few important body parts with special cushions.
Between joints
Since bones are hard on the outside, they need cartilage to cushion your joints, where bones connect and move together.
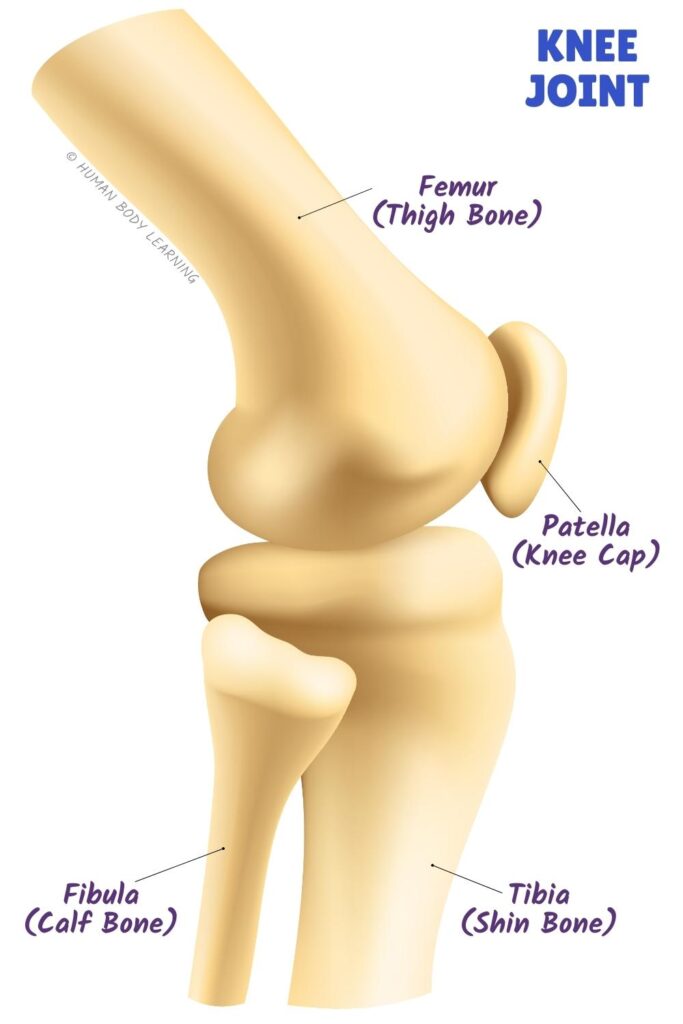
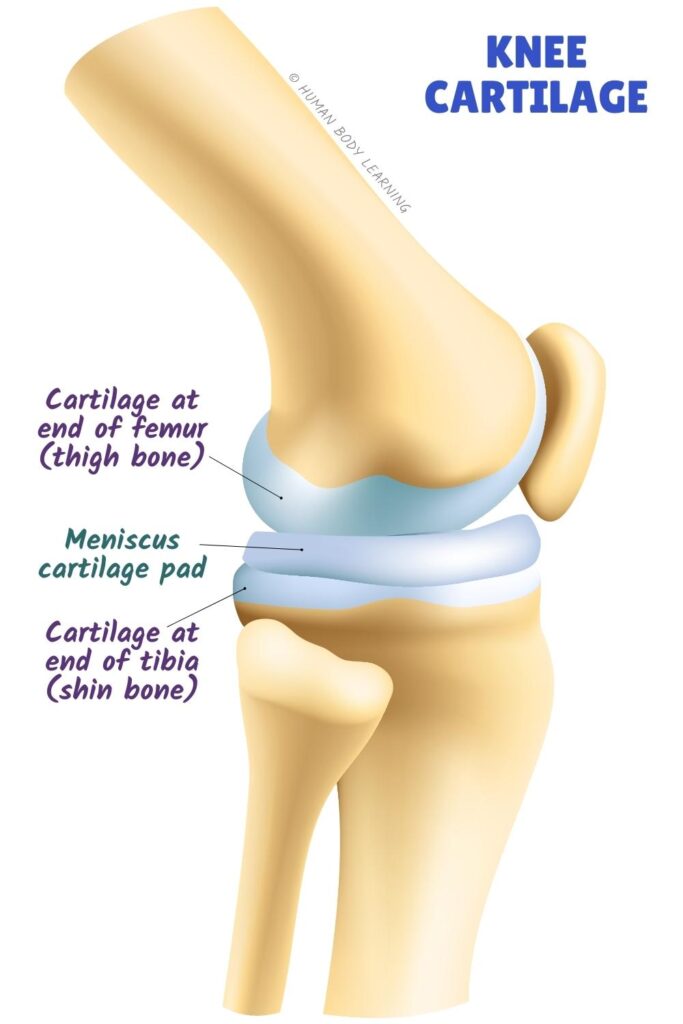
In the knee, cartilage can be found at the ends of the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). Since this joint carries your body weight when you walk, run, and jump, it needs extra support. The meniscus is an important pad of cartilage in your knee joint that acts like a shock absorber when you move.
In your spine, discs made of cartilage protect your vertebrae (backbone). These discs prevent each of the backbones from rubbing together.
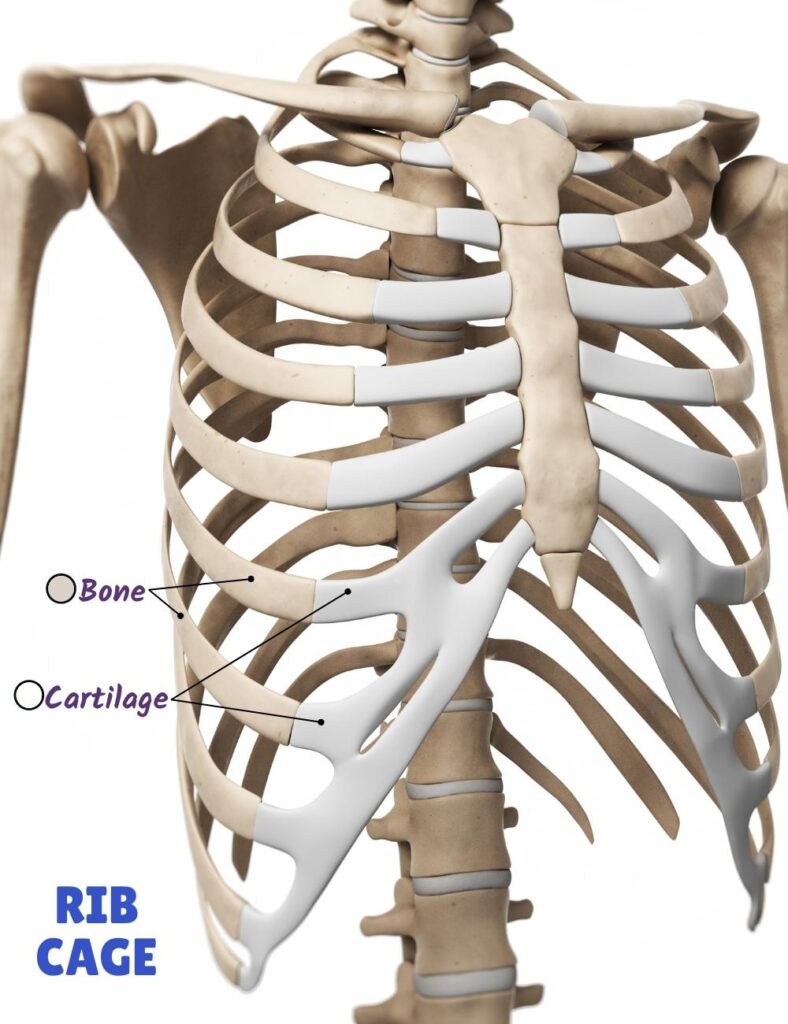
Rib cage
Because your lungs get bigger and smaller with each breath, your rib cage must also change size. This is why the rib cage needs so much flexible cartilage between the sternum and rib bones.
Nose and ears
Pinch your nose and tug on your ears! You can move these body parts thanks to the rubbery cartilage in your nose and ear.
Here’s a quick video that shows why the nose is so wiggly!
Growth plates
Growth plates are special growing zones that only kids have. They are made of cartilage and located near the ends of long bones, like the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone).
In growth plate areas, new cells are made, making your bones longer. This is how you grow taller!
Why do kids have more cartilage than adults?
Baby skeletons are mostly made of cartilage because they need to be more flexible. Before babies are born, they need to fit in a uterus and squeeze out of the birth canal.
It’s replaced by bone.
As children grow up, much of the cartilage in their body is replaced by harder bone. In other words, your skeleton anatomy transforms and hardens as you get older.
It wears down with age.
Over time, the cartilage in our joints gets worn down.
After many years of rubbing against hard bones, it breaks down and wears away. That’s why adults have less cartilage than kids.
What happens if your cartilage gets hurt?
Cartilage is the reason that kids can move around without pain. When it gets damaged, as grown-ups often experience, the back, knee, and other joints hurt.
Joints can also get busted from a hard fall or playing competitive sports, even in a young person. Ouch!
When cartilage is injured, the joint has less protective cushion, exposing the bone to stress and pressure. The chances of the bone breaking in this area go up.
Why is cartilage bad at healing?
Since cartilage has no nerves, it doesn’t hurt when damaged. If a person feels joint pain, the surrounding bones are damaged, too. The nerves in the bones send off painful warning signals.
Without blood vessels to bring fresh oxygen and nutrients, broken cartilage has trouble healing and growing back. That’s why you need to take good care of the natural cushions in your body.
Can doctors fix cartilage?
Yes! Surgeons can reattach or clean up little broken pieces of cartilage in a joint. Scientists are also researching ways to regenerate your body’s natural pillows from cells.
Sometimes, adults get knee or hip replacement surgeries to help their joints feel better. Surgeons put plastic caps at the ends of the damaged bones to make the joints move without pain.
3 ways to protect your cartilage
Learn more about your amazing bones!
Published on March 14, 2022. Updated on January 18, 2024 by Betty Choi, MD
Published on March 14, 2022. Updated on January 18, 2024 by Betty Choi, MD

Betty Choi, MD
Dr. Betty Choi is a Harvard-trained pediatrician who makes learning fun and doable. She created the kids’ anatomy book Human Body Learning Lab, which Science Magazine recommended as a “notable standout in the genre.”




